Feeds Overview
The Anchore Feed Service collects vulnerability and package data from the upstream sources and normalizes this data to be published as feeds that the Anchore Engine consumes.
The Anchore engine polls the feed service at a user defined interval, by default every six hours, and will download feed data updated since the last sync.
Anchore hosts a public service which provides access, for free, to all public feeds.
An on-premises feed service is available for commercial customers allowing the Anchore Engine to synchronize with a locally deployed feed service, without any reliance on the Anchore hosted service.
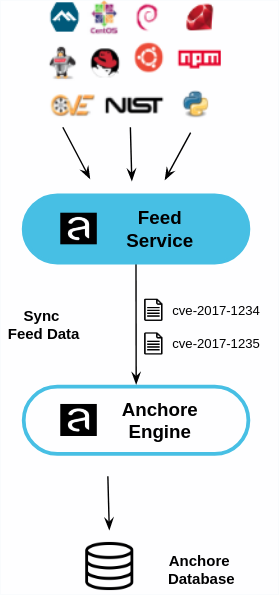
Sources and types of data are organized into feeds and groups.
- Feed - A grouping of similar types of data
- Feed Group - A namespace within each feed to allow more granular control of the sync process
Each feed can be independently configured to synchronize or not depending on what data your deployment needs. See configuration for more details.
Anchore Engine uses security vulnerability and package data from a number of sources:
vulnerabilities - security advisories from specific Linux Distribution vendors against Distribution specific packages.
- Alpine Linux
- CentOS
- Debian
- Oracle Linux
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat Universal Base Image (UBI)
- Ubuntu
- Amazon Linux 2
- Google Distroless
packages - Software Package Repositories
- RubyGems.org
- NPMJS.org
nvdv2 - NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
github - GitHub Advisories data retrieved by the GitHub API and used for matches against application packages
Third party feeds - additional data feeds are available for Anchore Enterprise Customers, see On-Premises Feeds Overview for more information.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.